Battery research: How can suspensions for electrode production or the electrolyte be characterized?
In the context of energy transition, battery research is becoming more and more important. They are now used in key areas such as portable electronic devices (smartphones, tablets, notebooks) as well as in the entire electromobility sector (electric cars, hybrid vehicles, electric wheelchairs). The most common systems currently used are lithium-ion NMC batteries (NMC: Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt).
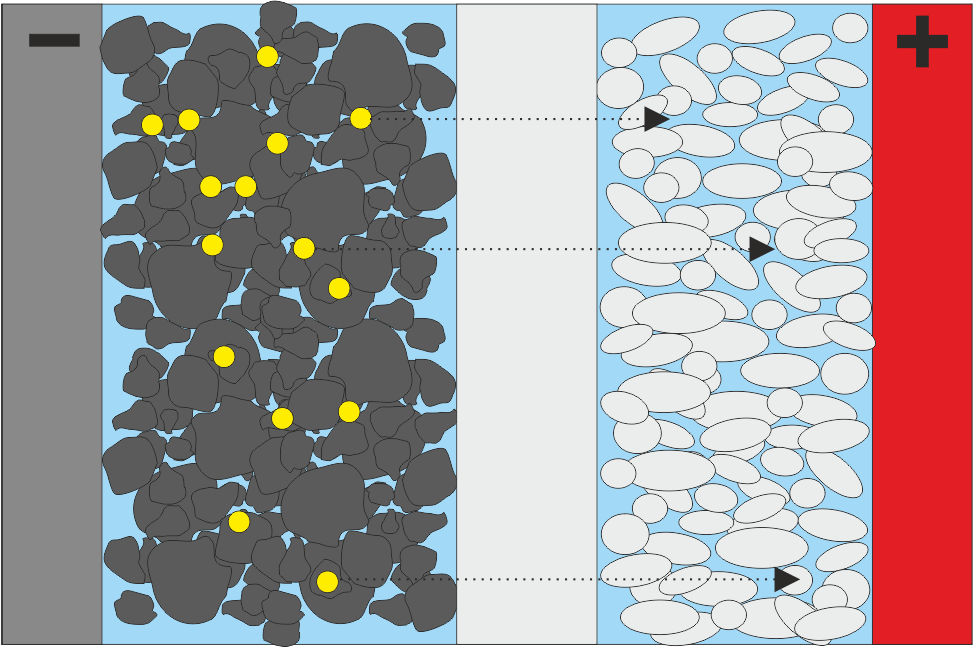
Scheme of an NMC accumulator
The manufacturing process of a modern accumulator is very complex and also includes numerous manufacturing steps in which organic solvents and generally liquid suspensions, i.e., hard material particles dispersed in a solvent, play an essential role. Particularly during processing, it is important that these systems are characterized in their original state with regard to properties such as particle size distribution, zeta potential or electrical conductivity in order to be able to assess the respective process step. It is precisely here that acoustic methods are available which in contrast to conventional optical methods such as static light scattering dynamic image analysis or electrophoresis can also be used in more concentrated dispersions.
How exactly the methods work and how the measurement results can be interpreted using the example of an NMC battery is explained in the following technical article:
Do you have further questions or need advice? Contact us:
Do you like our News?
Follow us:
 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English